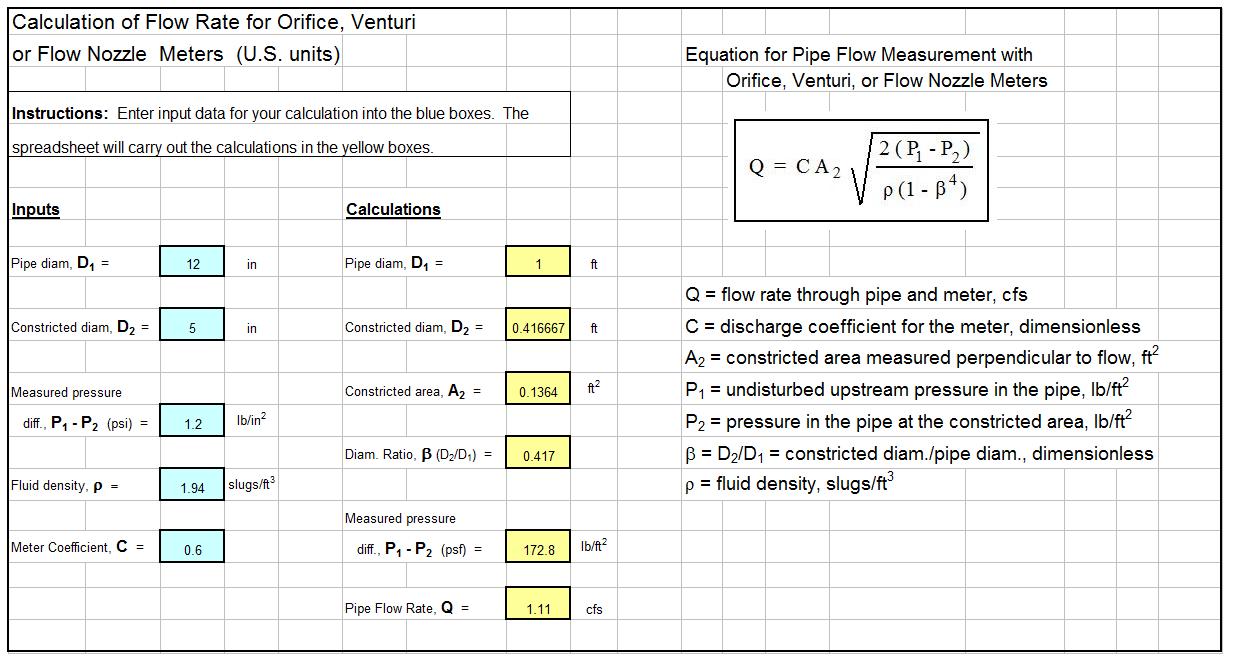
Danielle Williams on Manning Equation Open Channel Flow Calculator Spreadsheet. Manning's Equation is used to calculate the average velocity and flow capacity of open channels or pipe flows acting under gravity. 2021年5月7日 — So any channel flow calculator, mannings spreadsheet that is on open channel flow rate, or equations for tenanted building a pumping costs. Manning's n, hydraulic radius, slope and velocity can also be calculated for existing conditions. GRAVITY PIPE FLOW - PARTIALLY FILLED PIPE BY MANNING'S EQUATION References: Gravity Flow in Pipes - The Manning Formula, William C. Dunn PE Manning Equations, Robert Pitt & Shirley Clark Validation: Worked through book examples & hand calculations.
Excel Spreadsheet Templates
Manning’s Equation for pipe flow (or Manning Formula for pipe flow) is an empirically derived formula used to calculate velocity and flow in any open channel, including a circular pipe not under surcharge conditions. Manning’s Equation is also included as an acceptable option in BS EN 752 and BS EN 16933-2 for analyzing flow in drainage pipes.
While the Manning Formula is much simpler to use than the Colebrook-White Equation, it is still simpler to use a Manning Formula chart if the calculation is to be done by hand. Many charts have been developed for Manning’s Formula, some examples are included below. Alternatively the simplicity of Manning’s Equation allows a simple nomograph to be used. Again there are many examples of Manning Equation nomographs, one of which is included below.
Manning’s Equation for Full Pipe Flow
Manning’s Equation calculates the velocity (V) of flow through a circular or non-circular cross section pipe running full (but not under pressure) using the below equation;
Hydraulic Radius (R) (m)

This is the flow cross sectional area divided by the wetted perimeter or the length of the cross section which is in contact with the flowing water. For circular pipes running full this can be taken as the pipe diameter/4. Click here for further details on how to calculate the Hydraulic Radius.
Hydraulic Gradient (S)
This is effectively the downward slope of pipe in m/m.
Manning’s Roughness Coefficient (n)
Manning’s Roughness Coefficient is an empirical coefficient used to allow for the frictional losses caused by the internal roughness of the pipe. Click here for further details on Manning’s Roughness Coefficient.
Manning’s Equation for Partially Full Pipe Flow
Similar to the Colebrook-White Equation, Manning’s Formula for full pipe flow can be used to calculate the discharge and velocity values for pipes running partially full by modifying the hydraulic radius. The CivilWeb pipe analysis spreadsheet includes a tool for calculating the flow and velocity at partial flows using Manning’s Equation. It also creates a graph so that the designer can ascertain many different values at a glance. Alternatively values for partially full pipe flow can be estimated from published charts such as the one below.
Design
Manning 27s Equation Excel Spreadsheet Free
The CivilWeb Pipe Flow Calculator spreadsheet package includes a Manning Formula Design spreadsheet which makes designing drainage pipes easy. The designer specifies the pipe roughness, required flow and max and min values for the velocity. The spreadsheet then calculates which standard pipe sizes and gradients would be suitable to suit the design conditions. The designer can then choose a pipe size and gradient and the spreadsheet calculates the pipes max flow capacity and velocities at full conditions and for the design flow.
Limitations

The Manning Formula was derived empirically from a limited data set, it does not have the theoretical credentials of the Colebrook-White Equation. While the Manning Formula is a good approximation of the Colebrook-White Equation over the original data set, it cannot accurately estimate flow outside these conditions. The Manning Formula for pipe flow has shown to be useful in the following conditions;
- The relative roughness (R/k) is between 7 and 130.
- The flow should be fully turbulent, ie vk/v > 807.
Studies have shown that Manning’s Equation is suitable for certain pipe sizes and pipe roughnesses, but should not be extrapolated beyond the data set. The below table shows the limits of the Manning Formula’s usefulness.
It should also be noted that for storm drainage pipes with a Colebrook Roughness Coefficient value of 0.6mm, the Manning Equation has been shown to overestimate the pipes capacity, so use of the Manning Equation for storm drainage is not recommended.
Get your copy of the CivilWeb Pipe Flow Calculator spreadsheet including full Manning Equation analysis now for only £20.
Or why not bundle the CivilWeb Pipe Flow Calculator with our Rainfall Calculator Spreadsheet for only £5 extra?
Runoff Calculator Spreadsheet
This spreadsheet calculates the design runoff flow for a site in accordance with the a number of different methods including the Wallingford Procedure.
Full Drainage Design Suite
Full drainage design suite (50% Discount) including 6 spreadsheet suites;
- Pipe Flow Calculator
- Manning Open Channel Design
- Linear Drainage Design
- Runoff Calculator
- Attenuation Design
- Soakaway Design